Have you ever wondered about the true weight of words, particularly when choosing between "shall" and "should"? It's almost as if some words carry a bit more punch, a bit more commitment, in the way they are used. You know, these little words can really change what you mean to say, and that, is that, something we often overlook.
Today, we're going to explore "shall," a word that, quite honestly, has a very distinct presence in our language. We will look at its various shades of meaning, and how it stands apart from other words you might choose, like "should." This discussion, actually, will help clarify when to pick "shall" for your messages, making your communication much more precise.
Understanding these subtle differences is pretty important, especially when you want to convey something with real certainty or obligation. We'll explore how "shall" works, what it means, and when you absolutely, totally, should consider using it, based on its traditional usage and definitions.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Your Audience and Their Needs
- The Essence of "Shall"
- "Shall" Versus Other Modal Verbs
- People Often Ask About "Shall" or "Should"
Understanding Your Audience and Their Needs
When you consider words like "shall" or "should," you're probably someone who cares about how you express yourself. You might be a writer, a student learning English, or perhaps someone who deals with legal papers. You could be a professional who needs to be very clear in your instructions. The main concern, you know, often comes from wanting to pick the right word to get your point across without any confusion.
Many people find themselves wondering if "shall" is still used, or if "should" is always the better option. They might be asking, "When do I use 'shall' for something truly important?" or "What's the real difference between 'shall' and 'should'?" These are the kinds of thoughts that, honestly, prompt a closer look at these words. This discussion aims to clear up some of those questions, giving you a better handle on these sometimes puzzling terms.
You might be looking for ways to make your writing sound more official, or you might just want to speak with greater precision. This information is for anyone who values clear communication. It's for those who want to use words with purpose, making sure their message is received exactly as intended. So, it's pretty much for anyone who uses English and wants to use it well.
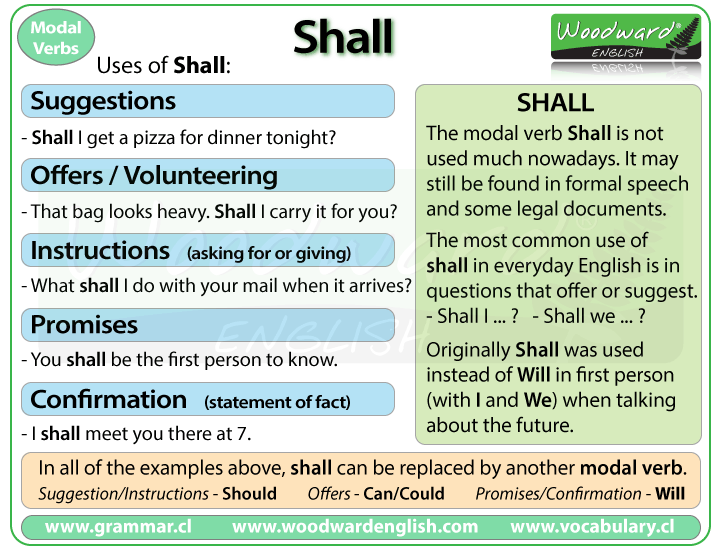
The Essence of "Shall"
The word "shall" holds a very specific place in the English language. It's a modal verb, a type of helper word that, you know, changes the meaning of the main verb. It is, in some respects, one of those words that can signal something about the future, about intentions, or even about rules. Its use has changed over time, but its core meanings remain quite powerful.
You might notice that "shall" is not as common in everyday talk today. However, it still appears in very important places. This word carries a sense of formality and, sometimes, a feeling of absolute certainty. It is, basically, a word that means business. We will explore its various uses, as described by those who study words.
"Shall" for Future Events
So, when we talk about the meaning of "shall," it often points to something that is, more or less, unavoidable. It's used to express things that seem very likely to happen. You know, it's about what is, in a way, destined for the future. This particular word, shall, often conveys a sense of certainty about events that are coming. It's not just a guess; it's something that truly feels set to occur.
It can describe something that will take place or exist in the future. This means, like, it's not a suggestion, but rather a statement of what is going to unfold. For example, if you say something "shall" happen, you are indicating a strong belief in its future occurrence. It gives a sense of inevitability, a feeling that things are already in motion and cannot be stopped.
"Shall" for Intent and Determination
"Shall" is often used to express intent. This means it shows what someone plans to do. It also expresses determination. So, it shows a strong will to do something. For instance, you might hear someone say, "I shall go to the store." This isn't just a simple plan; it shows a firm decision to go. It's like saying, "I am determined to do this thing."
Another example of this is, "She shall become the next queen." This sentence, you know, expresses a strong resolve or a firm prediction about her future role. It implies that her becoming queen is not just a possibility, but a determined outcome. This use of "shall" really highlights the speaker's conviction or a strong sense of purpose regarding the action.
"Shall" with "I" and "We"
Historically, "shall" was often used instead of "will" when the subject of the sentence was "I" or "we." This particular usage was, basically, a common way to talk about the future, especially in more formal settings. It was a standard practice that, you know, marked a certain style of speech and writing. This is a subtle difference that many English speakers learned.
Even today, you might find this use in very traditional or official documents. When you see "I shall" or "we shall," it often carries a slightly more formal tone than "I will" or "we will." It's a way of expressing future actions or intentions that, in a way, feels a bit more deliberate or even a little grand. It's a classic example of how language can add a layer of meaning.
"Shall" for Granting Permission
You use "shall," usually with "you," when you are telling someone that they will be able to do or have something they want. This is a very interesting use of the word. It's like giving an assurance or a promise. For example, if someone says, "Very well, if you want to go, go you shall," they are granting permission. They are confirming that the person's wish will be fulfilled.
This particular phrasing, "go you shall," sounds quite formal and, in a way, quite definitive. It is a strong affirmation. It's not just saying "you can go"; it's a more emphatic declaration that the action is allowed and will indeed happen. This use really shows "shall" acting as a guarantor of a desired outcome, which is, you know, pretty powerful.
"Shall" in Formal Contexts
"Shall" has some use in all persons, meaning with "he," "she," "it," "they," as well as "I" and "we." This is chiefly in formal writing or speaking. It is used to express determination. So, when you read "he shall" or "they shall" in a formal text, it often means there's a strong will or a fixed outcome involved. It lends a serious tone to the statement.
This means that even if you are not using "I" or "we," "shall" can still convey a sense of resolve or certainty in formal settings. It's a way of stating something that is not open to debate. It's a declaration that, basically, carries significant weight. This makes it a preferred choice in situations where clarity and authority are really important.
"Shall" in Laws and Directives
"Shall" also occurs in the language of laws and directives. This is where you see its meaning of obligation shine through very clearly. When a law states that something "shall" happen, it means it must happen. There is no room for choice or interpretation. It's a direct command or a mandatory requirement. This is, you know, why it's so common in legal texts.
For example, "The president shall hold office for five years." This sentence indicates a strict rule. It's not a suggestion; it's a binding condition. Similarly, "You use shall to indicate that something must happen, usually because of a rule or law." This highlights its role in defining what is required. It is, basically, a word of command in these contexts.
On the flip side, "You use shall not to indicate that something must not happen." This is equally firm. If a rule says you "shall not" do something, it means it is absolutely forbidden. There is no permission to do that action. This makes "shall" a very precise word for setting boundaries and establishing mandates, which is, you know, quite essential in legal documents.
"Shall" for Orders and Obligations
"Shall" can indicate an order. It can also show a promise. Furthermore, it points to a requirement or an obligation. So, when someone uses "shall" in this way, they are often giving a directive or making a solemn pledge. It's a word that conveys a sense of duty or a firm commitment, which is, you know, quite strong.
A good example of this is, "He shall answer for his misdeeds." This statement is not a gentle suggestion; it is a declaration of an unavoidable consequence. It means he is obligated to face the results of his actions. It's a very direct way of expressing accountability. This phrasing, actually, leaves no doubt about the expectation of justice.
"Shall" for Offers and Requests
The modal verb "shall" is used in English to express the future tense. It can also be used to offer suggestions. For instance, "Shall we go?" is a common way to suggest an action. It's a polite way to propose something. It invites a response, asking if the idea is agreeable. This is a softer use of "shall" compared to its use in laws, but it still has a formal feel.
It is also used to make formal requests. You might hear, "Shall I open the window?" This is a formal way to ask for permission or to offer help. It's a courteous inquiry. While its use has become less common in everyday English, this function of "shall" remains valid in more polite or traditional speech. It's a way to be very proper, you know.
"Shall" Versus Other Modal Verbs
The differences between "shall" and other modal verbs, like "should," are subtle. What is important to note is how "shall" conveys a strong sense of inevitability or obligation. It carries a weight that other words, which might suggest advice or simple possibility, do not. So, when you pick "shall," you are sending a very clear message about certainty or a requirement.
When you consider a word like "should," it typically suggests something that is advisable or recommended. For instance, "You should eat your vegetables" is a piece of advice. It's not a command. It implies that doing so would be a good idea, or that it is the proper thing to do. This is a very different kind of message compared to "shall."
In contrast, "shall" often implies a mandate or a firm prediction. When someone says, "This shall be done," they are not offering a suggestion. They are stating a certainty or a directive. This distinct difference means that choosing "shall" makes your statement much more forceful. It removes the element of choice or recommendation, replacing it with a sense of certainty or duty.
So, if you want to express something that must happen, or something that is a firm intent, "shall" is a strong choice. If you are offering advice, or talking about what is a good idea, you would typically use a different word. This distinction is, you know, key to clear communication, especially in formal settings or when conveying serious commitments.
Understanding these distinctions helps you use language with greater precision. It allows you to select the word that perfectly matches the level of certainty or obligation you wish to convey. So, next time you are crafting an important message, think about the subtle yet significant impact of "shall" compared to other options. It really makes a difference, actually, in how your words are received.
People Often Ask About "Shall" or "Should"
Here are some common questions people have about these words:
1. Is "shall" still used today?
Yes, "shall" is still used today, especially in formal writing and speaking. It is very common in legal documents, rules, and official directives. While it's less frequent in everyday conversation, it maintains a strong presence in contexts where precision and obligation are key. So, it's not gone; it just lives in different places.
2. What is the main difference between "shall" and "should"?
"Shall" often expresses a strong sense of obligation, determination, or inevitability, particularly in formal settings. It means something "must" or "will certainly" happen. "Should," on the other hand, typically expresses advice, recommendation, or what is proper. It suggests something "ought to" happen, but without the same level of command or certainty as "shall."
3. When should I choose "shall" over "will"?
You might choose "shall" over "will" when you want to convey a stronger sense of determination or a formal promise, especially when the subject is "I" or "we." In legal or official contexts, "shall" is used to express a requirement or a mandate, indicating something that is absolutely necessary. It gives a statement more weight and a feeling of certainty, which is, you know, quite important.
For more insights into English grammar, you can check out resources like Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary. Learn more about modal verbs on our site, and link to this page for more grammar rules.


Detail Author:
- Name : Joanne Gulgowski
- Username : izabella91
- Email : abergstrom@reinger.com
- Birthdate : 1978-03-08
- Address : 5072 Arden Spring Ralphhaven, OH 76536-2382
- Phone : 253.664.8586
- Company : Cruickshank, Price and King
- Job : Preschool Education Administrators
- Bio : Ex dolore quasi odio facere. Et similique et exercitationem accusamus. Est dolorum porro optio ea sunt ex alias et.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/krystal_parker
- username : krystal_parker
- bio : Saepe nostrum eveniet sed.
- followers : 6009
- following : 761
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/krystal_dev
- username : krystal_dev
- bio : Harum dolores et cumque unde eum blanditiis.
- followers : 6902
- following : 584
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/krystal_official
- username : krystal_official
- bio : Quae tempora necessitatibus eveniet. Id magni aut id et ea molestiae.
- followers : 6510
- following : 1984

