Have you ever felt a bit lost in the world of digital security, especially when dealing with those mysterious file extensions like .PEM? Perhaps you've even jokingly called them "pem pem norgay" in your head to remember them, like a little secret code. Well, you're certainly not alone if these file types seem a little confusing at first glance. They are, in fact, pretty important for keeping our online interactions safe and sound.
These files are actually at the heart of how websites prove who they are, how your emails stay private, and how data moves securely across the internet. We interact with them more often than we might realize, even if we don't directly open them up ourselves. So, understanding what they do can really help you out, especially if you're working with digital systems or just curious about how things tick.
This article will shed some light on what a .PEM file truly is, how it works, and how it relates to other common certificate formats. We will also look at how tools like OpenSSL can help you manage them. By the end, that "pem pem norgay" will seem much clearer, and you'll have a better grip on these essential digital pieces, as a matter of fact.
Table of Contents
- What's the Deal with Pem Pem Norgay?
- Unraveling the .PEM File Mystery
- OpenSSL and Your .PEM Files
- Spotting a .PEM File: How to Check
- Deciphering Common SSL File Extensions
- Converting Your Certificate Files
- Frequently Asked Questions About Digital Certificates
- Keeping Up with Digital Certificate Standards
- Final Thoughts on Pem Pem Norgay
What's the Deal with Pem Pem Norgay?
So, you might be wondering, what exactly is "pem pem norgay"? Well, it's really just a fun way to say .PEM, the file extension. This little phrase helps us remember something quite important in the world of digital certificates. It helps us talk about those files that are key for secure communication. You see, they hold vital pieces of information that make the internet a safer place for all of us, literally.
When we talk about .PEM files, we are talking about a very common format for storing cryptographic data. This data often includes things like public keys, private keys, and server certificates. They are a fundamental part of how secure connections are made. For instance, when you visit a website with "https" in the address, a .PEM file, or something similar, is probably involved in making that connection safe, you know?
Understanding these files is pretty useful, especially if you work with web servers, secure applications, or anything that needs to prove its identity online. It helps you troubleshoot issues and set up secure systems properly. So, while "pem pem norgay" sounds a bit playful, the topic itself is quite serious and practical, to be honest.
Unraveling the .PEM File Mystery
A .PEM file is not just a random collection of letters and numbers. It stands for "Privacy-Enhanced Mail," which was an early standard for secure email. Even though its original use has changed, the file format stuck around for other things. It's a very common way to store various pieces of digital certificate information, actually.
What makes a .PEM file special is its human-readable format. This means you can often open it with a simple text editor and see what's inside. This is a big help when you need to quickly check something or copy parts of a certificate. It's a bit like looking at a plain text document, but with a lot of coded information, you know?
These files are pretty versatile. They can hold a single certificate, a chain of certificates, or even a private key. This flexibility is why they are so widely used across different systems. It's really quite a adaptable format for digital security needs, in a way.
Textual Encoding Explained
At its heart, a .PEM file uses textual encoding. This means the binary data, which computers understand, is converted into plain text characters. This conversion makes it much easier to move these files around, like copying and pasting them into configuration files or sending them via email. It's a bit like translating a secret code into a more common language for easier sharing, more or less.
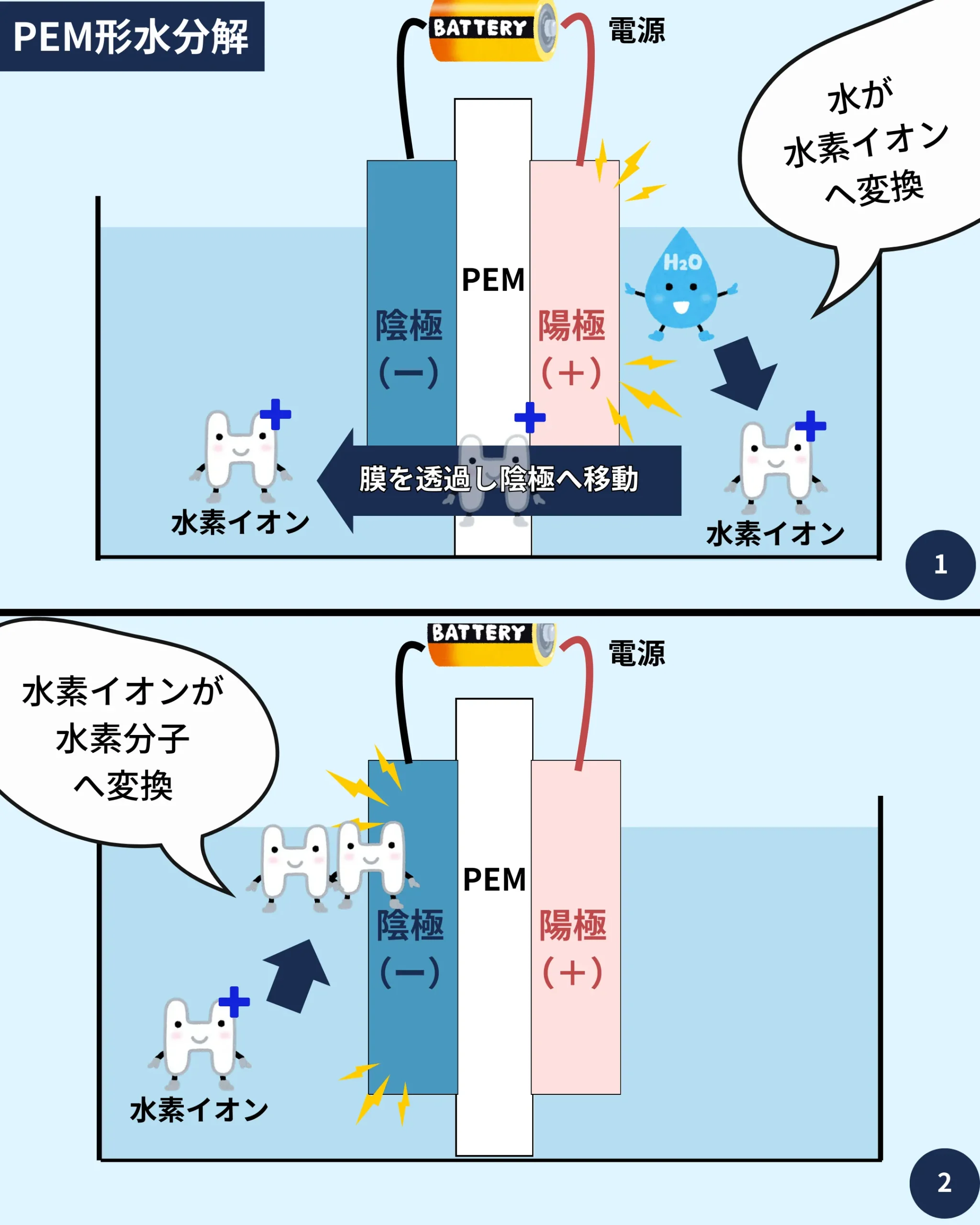
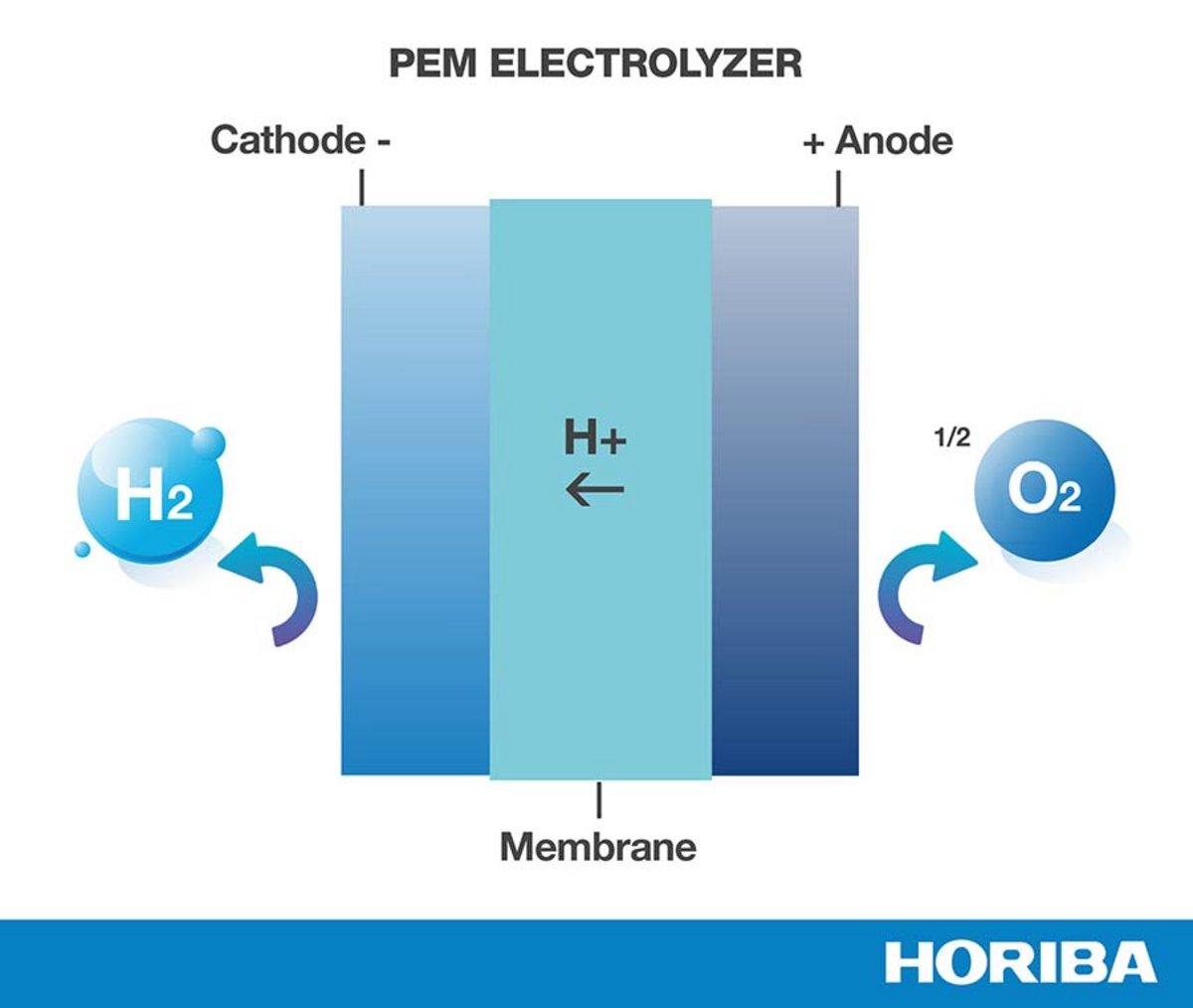
The most common form of this textual encoding is Base64. You will often see .PEM files start with lines like "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----" and end with "-----END CERTIFICATE-----". Everything between these lines is the Base64-encoded data. This structure clearly marks the beginning and end of the important information, which is quite helpful, you see.
This textual approach is a big reason why .PEM files are so popular. Unlike some other formats that are purely binary, .PEM files offer a way for humans to inspect their contents, at least partially. This makes troubleshooting and managing certificates much less of a headache for system administrators and developers, frankly.
The Many Faces of .PEM
The interesting thing about a .PEM file is that what's inside can vary a lot. A .PEM file is just a container, so to speak, for different types of cryptographic items. It could contain a public certificate, a private key, a certificate signing request (CSR), or even a certificate chain. This means the same file extension can mean very different things depending on its contents, which is slightly confusing at times.
For example, a .PEM file might hold just your server's public certificate. Another .PEM file could contain your private key, which you must keep very safe. Yet another might have a bundle of certificates, including your server certificate and any intermediate certificates needed to establish trust. It's like a general-purpose box that can hold various valuable digital items, you know?
Because of this flexibility, it's important to know what kind of information a specific .PEM file is supposed to contain. This often depends on the context in which you received it or how it was generated. Checking the file's header lines, like "BEGIN PRIVATE KEY" or "BEGIN CERTIFICATE," can give you a pretty good clue, as a matter of fact.
OpenSSL and Your .PEM Files
OpenSSL is a powerful, open-source command-line tool. It's pretty much the go-to utility for working with SSL/TLS certificates and keys. If you need to create, convert, or inspect .PEM files, OpenSSL is probably what you'll use. It's a very versatile program for anyone dealing with digital security assets, actually.
This tool can handle a wide array of cryptographic tasks. It can generate private keys, create certificate signing requests, and manage certificates in various formats, including .PEM. Learning a few basic OpenSSL commands can save you a lot of time and trouble when you're managing your digital security infrastructure, you know?
Many system administrators and developers rely on OpenSSL every day. It allows for fine-grained control over cryptographic operations. So, if you're looking to work more deeply with your "pem pem norgay" files, getting comfortable with OpenSSL is a pretty smart move, to be honest.
Making a .PEM File with OpenSSL
One common task is creating a .PEM file from an existing SSL certificate or even generating a new one. OpenSSL can easily take a certificate in another format and convert it into a .PEM file. This is super handy when you have files from different sources and need them all in a consistent format for your system, you see.
For instance, if you have a certificate in a binary format, OpenSSL can transform it into the text-based .PEM format. This process often involves specifying the input file and the desired output format. The command lines are usually quite straightforward once you get the hang of them. It's a bit like telling the computer exactly what kind of file you want, you know?
You can also use OpenSSL to create a .PEM file that contains both a public certificate and its corresponding private key. This is a common setup for web servers. This combined file is often used to quickly deploy a certificate. It's a very efficient way to bundle necessary components together, in a way.
Splitting and Joining .PEM Files
Sometimes, you might receive a single .PEM file that contains several different items, like a certificate chain. This means it has your server certificate, plus any intermediate certificates from the certificate authority. You might need to split these into individual files for certain applications, or perhaps consolidate separate files into one. This is where OpenSSL really shines, actually.
If you have a .PEM file with multiple certificates, you can use OpenSSL commands or even just a text editor to separate them. Each certificate will have its own "BEGIN CERTIFICATE" and "END CERTIFICATE" markers. You can simply copy and paste each block into its own new file. It's like taking a stack of papers and giving each one its own folder, you know?
Conversely, if you have several individual .PEM files – say, one for your server certificate and another for an intermediate certificate – you can combine them into a single .PEM file. This is often done by simply concatenating the text contents of the files. This can be very useful for systems that expect a full certificate chain in one file. It's a pretty flexible approach, to be honest.
Spotting a .PEM File: How to Check
You might have a file and not be sure if it's in .PEM format. This is a pretty common situation. Luckily, there are a few simple ways to check. Knowing how to identify a .PEM file quickly can save you a lot of guesswork and potential errors when configuring systems, you see.
The easiest way to check is to open the file with a text editor, like Notepad on Windows or TextEdit on Mac. If it's a .PEM file, you will see human-readable text. Look for those distinctive "BEGIN" and "END" lines, such as "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----" or "-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----". These markers are a dead giveaway, actually.
If you open the file and see a jumble of unreadable characters, it's probably in a binary format, like .DER. In that case, you would need to convert it to .PEM using a tool like OpenSSL if you want to see its contents in a text editor. It's a very quick visual check that often provides the answer you need, you know?
Also, if you're using a Linux or macOS system, you can use the `file` command in the terminal. This command often gives you information about the file type. For example, `file your_certificate.pem` might tell you it's "PEM certificate" or similar. This is a pretty reliable method for quick identification, as a matter of fact.
Deciphering Common SSL File Extensions
Beyond "pem pem norgay," you'll often encounter other file extensions related to SSL certificates. These include .CER and .DER. While they all deal with X.509 v3 certificates, their encoding and typical usage can differ. Understanding these differences helps you pick the right file for the right job, you see.
An X.509 v3 certificate is a standard format for public key certificates. It's like a digital ID card. These certificates are used to verify the identity of a website, person, or device. All .PEM, .CER, and .DER files can contain an X.509 v3 certificate, but they present the information in slightly different ways. It's a very important standard for digital trust, actually.
Knowing which extension means what can prevent a lot of headaches when you're setting up servers or applications. Some systems might prefer one format over another. So, being able to distinguish them is a valuable skill for anyone working with digital security, to be honest.
.PEM, .CER, and .DER: What's the Difference?
Let's break down the common formats: .PEM, .CER, and .DER. As we've discussed, .PEM is the textual encoding, usually Base64, with those "BEGIN" and "END" markers. It's widely used because of its readability and ease of transfer. It's a pretty versatile format, you know?
A .CER file is often just another name for a .CRT file, and it can be in either .PEM or .DER format. Typically, when you download a certificate from a browser or a certificate authority, it might come as a .CER file. It's a bit like how a document might be called a "report" but could be a .DOCX or a .PDF, more or less.
The .DER extension, on the other hand, always signifies a binary encoding. This means the data is not human-readable; it's in a raw, compact form. .DER files are often used in Java environments and sometimes for specific hardware devices that prefer binary formats. They are generally smaller than their .PEM counterparts because there's no Base64 overhead. So, it's a very different way of storing the same data, actually.
The .DER Encoding Method
The .DER extension represents the Distinguished Encoding Rules method of encoding data. This is a specific way of structuring and encoding the raw binary information that makes up a certificate or key. It's a precise set of rules that ensures the data is interpreted correctly by machines, you see.
When you have a .DER file, it's not meant for human eyes. You can't open it in a text editor and make sense of it. Instead, software applications read and process these files directly. This makes them efficient for machine-to-machine communication where file size and parsing speed are important. It's a pretty streamlined way to handle data, in a way.
Converting between .DER and .PEM is a common task using OpenSSL. For example, you might receive a certificate in .DER format and need to convert it to .PEM for use on a Linux server. OpenSSL handles this conversion smoothly, allowing you to bridge the gap between different system requirements, which is quite handy, to be honest.
Converting Your Certificate Files
It's pretty common to find yourself with certificate files in one format but needing them in another. This often happens when you're moving certificates between different operating systems or software applications. Fortunately, converting between formats like .CRT and .PEM is usually a simple process, especially with the right tools, you know?
The key thing to remember is that the underlying certificate data is the same, regardless of the file extension or encoding. The conversion process simply changes how that data is presented. It's a bit like having the same book available in both a paperback and an e-book format. The story is identical, but the way you read it differs, more or less.
Being able to convert files quickly helps you maintain flexibility in your digital security setup. It means you're not stuck if a particular system only accepts one specific file type. So, mastering these conversion steps is a very practical skill for anyone in IT, actually.
From .CRT to .PEM: A Simple Switch
Often, .CRT files are already in .PEM format. The .CRT extension itself doesn't tell you the encoding. It just indicates that the file contains a certificate. If you open a .CRT file in a text editor and see the "BEGIN CERTIFICATE" and "END CERTIFICATE" lines, then it's already a .PEM file. You might just need to rename the file extension to .PEM, which is quite simple, you see.
If your .CRT file is in a binary format (like .DER), then you'll need to use OpenSSL to convert it. The command for this is pretty straightforward. You'll specify the input file (your .CRT file) and tell OpenSSL to output it as a .PEM file. This process effectively decodes
Detail Author:
- Name : Guido Goyette
- Username : parker.aron
- Email : raul.hansen@willms.net
- Birthdate : 1990-05-27
- Address : 8958 Rupert Knolls Suite 980 South Germaineburgh, WI 82860
- Phone : +1.551.706.4355
- Company : Cormier, Harber and Gaylord
- Job : Metal Fabricator
- Bio : Iste illum impedit eos itaque dolor. Quaerat ut consequatur id ut et. Illo occaecati est blanditiis aut non.
Socials
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/icie_dev
- username : icie_dev
- bio : Dolore dolorem quis expedita voluptatem iusto. Enim quidem et quia est.
- followers : 498
- following : 2611
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/willmsi
- username : willmsi
- bio : Est eveniet nostrum eum enim sit dolores. Sit qui et autem eaque vel. Et et tempora in non.
- followers : 2124
- following : 2638

